2026 Author: Erin Ralphs | ralphs@carsalmanac.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 21:14:18
Let's consider in a short article the basic practical data about an interesting device that measures the number of revolutions, its application and operation.
Tachometer: what is it?
Many technical systems contain rotating parts. It is often necessary to know at what speed they are spinning, whether it corresponds to the norm, etc. For this, a special device called a tachometer was invented. In fact, it allows you to measure the speed of rotation, so that you can then process this parameter in order to control and correct if necessary.

Tachometer operation is usually presented in the form of visual data either on a digital display or on an analog dial gauge. Most people who are not very familiar with this word have most likely observed it in their own vehicle. Since very often the dashboard of a car is supplied with just a tachometer.
By the way, this word literally translates from Greek as “speed measurement”. And although now in cars the main instrument for detecting speed is the speedometer, however, the tachometer safely continues to coexist with the first one on the panel of almost any modern vehicle.means, while performing another important function.
The simplest device
The simplest tachometer circuit is a banal counter of the number of revolutions of a rotating part in any technical system. It can be a machine tool, a turbine, a shaft of a drilling rig, and much more. In any case, the simplest diagram will show only the number of revolutions of this very part. And already with a good stopwatch, you can calculate the average value of the rotation speed for the considered period of time.
The simplest tachometer circuit is shown in the figure. It uses a photo sensor that receives a signal from a stroboscope mounted on the motor shaft. The data obtained in this way from the photosensitive transistor is fed to the microcircuit, which then outputs them in digital format on a special display.

Classification
Separation is easiest to carry out according to the principle of operation of the device itself. There are quite a few of them, let's consider the most common ones. First, magnetic induction. Here the basic principle is the induction of an eddy current in a metal body, the magnitude of which depends on the speed of rotation. Secondly, electric tachometers. They use the dependence of the output voltage parameters on the rotational speed. Thirdly, photovoltaic, where the light flux is modulated. Finally, capacitive tachometers use the dependence of this value on the speed of rotation. There are others. Trying to simply answer the question: "Tachometer: what is it?", We will not go into the complex jungle of all physicalprinciples that can be used to measure the angular velocity of rotating bodies.
Auto
In the automotive industry, the measurement of the number of revolutions of rotating parts is actively used. For example, the angular velocity of the crankshaft is important to know, since the driver should not drive the engine into overload mode, unless, of course, he is Schumacher on the Formula 1 track. Also, knowing when to upshift or downshift is very helpful, again in terms of increasing engine life.

By the way, when it comes to racing, tachometer RPM is even more important here. Since, although the engine is constantly running in extreme mode, its resource must also be protected, however, within completely different time limits. And again, by knowing when it's not too late to upshift. Otherwise, you can simply not get to the finish line, being on the sidelines with a burning or jammed engine.
Application
The most widely used this device is still in mechanical engineering. The tachometer for the motor is used when measuring the speed of the crankshaft. Internal combustion engines of the vast majority of transport equipment in the service of man are equipped with this useful device. This includes, of course, cars, as well as aircraft, diesel locomotives, tractors, ships and some others.

Another important application for tachometers is to controlthe speed of rotation of parts of various technological machines, such as machine tools, drilling equipment, etc. Finally, the last and already somewhat indirect use of such devices is the counting of the number of pulses in conveyor technical processes. For example, some raw materials or materials are moving along the line, and you need to know how much has passed and how much more is needed. It can also be used to control the operating time of any equipment in the run-in mode or during technical tests.
Analog or digital?
Answering the question: "Tachometer: what is it?", We have not considered another important point. Representation of data transmitted by the sensor of the device to the control cabin of the vehicle or on the scoreboard of the machine or other technological equipment in which it can be used. Ever since the advent of the tachometer, the analog principle of data presentation has been used on car panels. At least for the simple reason that there was no digital way in those distant times. Apparently, therefore, it is much easier for the driver of a modern car to see an arrow showing how many revolutions his engine gives out and how far it is to the red zone. It is familiar and visual.

The digital era has brought tachometers that show the number of revolutions on the scoreboard as a constantly changing value. This representation somewhat complicates the perception of the actual value of the number of revolutions. This is aggravated by the fact that the data on the digital block is constantly changing, in contrast to the arrowpointer, which gives an average value that changes more smoothly. Therefore, an automobile tachometer is usually analog. What it is, we hope, we managed to understand from the corresponding section.

Summarize the question posed by the title. In the battle of "analogue" against "digital", the former clearly wins for the average motorist who does not need to know the value of the number of revolutions with an accuracy of 100 rpm in every second of his time behind the wheel. But with various adjustments, for example, electronic components, the “digit” ignition is out of competition, because it gives the engineer the necessary accuracy.
Conclusion
Having asked the question in the article: “Tachometer: what is it?”, We found out its main purpose, application, some principles underlying the work. In general, the device is not only useful, but simply necessary for the correct operation of various technical systems using rotating parts.
Recommended:
Double clutch: device and principle of operation
Along with the new trends in the development of "green" technologies, the automotive industry is currently experiencing no less interesting changes in terms of approaches to the development of traditional structural parts of the car. This applies not only to the design of the internal combustion engine and the inclusion of more reliable materials, but also to the control mechanics
How airbags work in a car: device and principle of operation
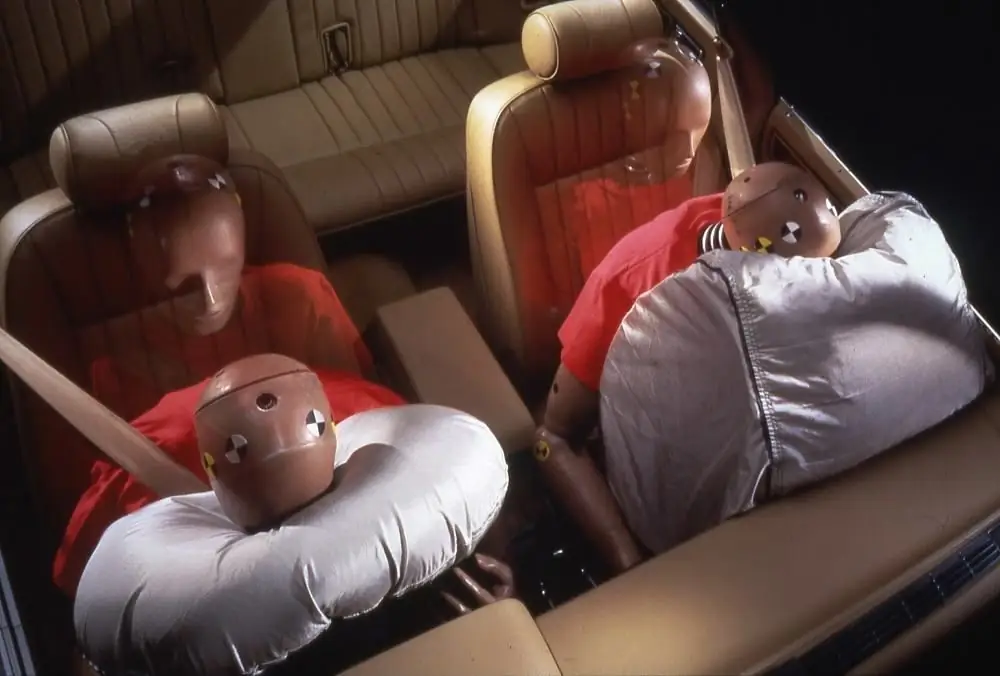

Modern cars are equipped with many protective systems, including airbags. They allow you to avoid serious consequences for the driver and passengers (depending on the configuration). Moreover, their number varies from 2 to 7 pieces, but there are models where there are 8, 9, or even 10 of them. But how does an airbag work? This will be of interest to many motorists, especially inquisitive individuals who want to be well versed in their car
Idle speed sensor - purpose and function

Any car is made up of many parts. Each of them carries a function, and a malfunction of at least one mechanism can lead to a series of breakdowns. One of the important details is the idle speed sensor, which will be discussed in the article
How to make a tachometer with your own hands?

DIY tachometer: recommendations, possibilities, material, diagram. How to make a car tachometer with your own hands?
Valve cover gasket: design, function and replacement

When a valve cover gasket fails, car owners should brace themselves for big trouble. The fact is that this spare part provides absolute tightness to the engine. Therefore, as soon as the gasket loses its sealing properties, the motor starts to flow

