2026 Author: Erin Ralphs | ralphs@carsalmanac.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 21:14:09
It's a paradox, but with today's level of technology development, especially in the automotive industry, engineers from all over the world have not been able to come to a single opinion about the transmission. A mechanism has not yet been created that meets the following requirements - compact dimensions and light weight, a serious power range, no significant loss of torque, saving fuel, comfort of movement, decent dynamics, resource. There is no such unit yet, but there is a robotic box. She, though not completely, but meets many of the above requirements.
Economy class
These mechanisms do not differ from traditional mechanics in their design and principle of operation. But the gears and clutch are engaged by means of electric or hydraulic actuators. Although, this is very general. Indeed, between the five-speed Easytronic from Opel and the 7-speed roboticbox from Ferrari, in addition to the number of steps, a huge number of technological solutions and there is also a difference in electronic tuning. Yes, and constructively in these two options there are a lot of fundamental differences. And installing them on specific cars had different goals.

The first robotic boxes on serial models began to appear only at the beginning of the last century. Their recipe is quite simple - they took ordinary proven mechanics with a classic clutch. Then all this was supplemented by electric drives that squeezed the clutch disc and shifted gears according to a certain algorithm. So, Toyota introduced the Multimod transmission system, the Ford robotic box was called Durashift, Honda introduced Ishift. The market sometimes presented several models at the same time - it was a kind of boom. What caused it? There is only one answer to this question - savings.

For those who bought the Corolla, Peugeot 207, Ford Fusion and other models and did not want to shift gears manually, the automakers offered an inexpensive analogue of the traditional torque converter and CVT. After all, several servos bolted to a well-functioning base are much cheaper than a pure automatic or CVT.
Jerking and pushing
The marketing ploy and experiment of the engineers failed. Cars equipped with a robotic box, as it turned out in reality, only likeunassuming drivers. The thing is that such cars start in the same way as beginners who have just graduated from a driving school - with jerks and jerks. And most importantly, what is even worse - there are delays when switching.
To disengage the driven disc from the flywheel, select the desired gear and restore torque, the robot needed more time than the average driver on a manual transmission. In addition, robots can make mistakes in steps. Therefore, a jerky driving mode, completing an overtaking in the required gear, or simply the process of organically infusing into the stream for "robots" is a big test.
Owner Reviews
More reviews of the robotic box indicate the faulty reliability of these units. Often the electronics fail, the boxes heat up, the clutch life is reduced compared to ordinary mechanics. The lack of a "Parking" mode is the smallest of all troubles.
Today, "robots" with a single-plate clutch are installed only on French cars. But it must be said that this negative experience did not alienate most manufacturers from such transmissions. Those who relied on these checkpoints radically revised their design, having previously studied the history of "robots".
Device
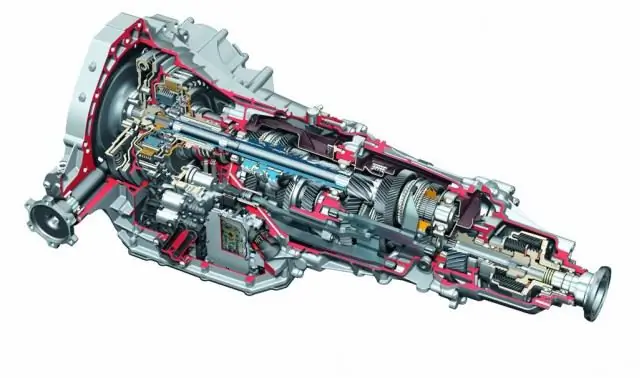
These mechanisms are arranged quite simply. In fact, this is a regular manual transmission with additional elements. These drive elements activate and deactivate the clutch, as well as change gears. The principle of operation of the mechanics and the "robot" are the same.

However, there are minor differences. The main difference isthese same executive devices. They control the clutch. The operation of the activators is controlled by an electronic control unit. As for the clutch, it can be used as a single disc, several discs or a package of friction elements. Now one of the progressive solutions is the dual clutch system.
Drive types
Manual gearboxes can be equipped with a hydraulic or electric drive. In the case of electric, servo drives are used as actuators. It is an electric motor with mechanical gears. The hydraulic drive works on the basis of hydraulic cylinders and electromagnetic valves.
Electric drive features slower speed and lower power consumption. In hydraulic systems, it is necessary to constantly maintain pressure, and this requires a lot of energy. But the operation of hydraulic robotic gearboxes is much faster. Some hydraulic manual transmissions on sports cars boast lightning-fast shift speeds.
These qualities determine the use of manual transmission with electric drive on budget car models. As an example, a robotic box on Lada-Vest. Gearboxes for more expensive car models are equipped with hydraulic drive.
Operation principle
The mechanism operates in one of two modes - automatic or semi-automatic. In the first case, the ECU, based on the signals received from the sensors, implements a control algorithm through actuators.

Regardless of the modelGearbox, they have a certain switching mode. The operation of the box in this mode allows you to shift gears manually using the selector or paddle shifters.
Dual clutch gearbox
The evolution of these gearboxes has been turned almost upside down. The simplest single clutch solutions only started to appear at the beginning of the 21st century. However, even 60 years before that, a patent was received for a manual transmission with two clutches. There were no sketches then, but it was already proposed to install this transmission on a 1934 Citroen Traction Avant. It was technically impossible and the idea was safely forgotten.
The birth of the DSG
The idea was revived in the German company Porsche. In the 80s, this company actively participated in circuit racing competitions. It was for these competitions that a transmission with two clutches was created. Prototypes then showed good results. The unit turned out to be very heavy, huge and unreliable. Repair of a robotic box in those conditions was very expensive, and they decided to abandon the checkpoint. She didn't settle down. But it was the ancestor of the modern DSG robotic transmission.
Multiply by two
Technically and technologically, all this is built on the principle of manual transmission - the device does not have planetary gear sets, friction packs, belts and chains. The two drive shafts are in each other. Each has its own separate clutch. On the driven shafts there are gears and synchronizers familiar to the manual transmission.
Each drive shaft, together with its clutch, is responsible for its own range of gears. One for even, one for odd. While the carpicks up speed at one stage, the next one is already on - the necessary gears are connected to synchronizers. When you need to go down or up, one clutch opens and the second closes.
This ensures a high gear change speed. In some models, switching takes no more than 0.1 seconds. There are no hydraulic losses here, and compared to CVTs, "robots" can digest more serious torque.
But these units are not perfect, and the repair of robotic boxes of this kind can be expensive. In order for the mechanism to have a reserve of torque, you need a fluid in which the clutches work. It has frictional properties and cools the assembly. This fluid reduces efficiency. Also, energy is needed to operate the pump, which creates pressure in hydraulic drives. For a powerful engine, this is not important, but compact power units do not allow you to see the advantages of such boxes over automatic transmissions.

In 2008, VAG managed to get around this problem. There was a model with dry clutches. The pump only runs when needed. Due to the presence of seven steps, the mechanism turned out to be easier. But the torque that this box can handle is up to 250 Nm.
Wet is unreliable
It is believed that wet clutch robotic gearboxes are more durable and resourceful than their dry counterparts. In theory, this is so. But on early models from VAG, robotic gearboxes were often repaired due to clutch failure. Was to blameflywheel.

Also often, DSG owners become pedestrians for a while due to the combustion of mechatronics. It is very expensive to change it. Debris during clutch operation clogs the filters and enters the control unit. Solenoids fail.
But the DQ 250 box is quite reliable. Especially if it is paired with a not too powerful engine. If the owner drives calmly, then the service life will be long, provided that the transmission fluid is changed regularly.
Dry is not always comfortable
Resource DQ 250 is gradually being replaced today. Mass models from the Volkswagen-Audi concern are now equipped with 7-speed dry DSGs. The mechanism is less expensive. But you will have to pay for this with a clang, vibrations. In urban conditions, the mechatronics constantly overheats. The clutch wears out after 50 thousand kilometers.

Repair of a robotic gearbox and the purchase of spare parts for it is a problem. The clutch unit will cost 70 thousand rubles. On later models, there are problems with the clutch fork. sometimes you need to change the firmware. The machine behaves the same unstable, but the aggregate part is intact.
Conclusion
These were all shortcomings of the DSG. AvtoVAZ, on the other hand, installs completely different robots with one clutch on Vesta and Grants. They are thoughtful, they twitch, but they don't have problems like German checkpoints.
Recommended:
"Nissan" (electric car): specifications, operating features, reviews

"Nissan" (electric car) is known to buyers as the Nissan LEAF. This is a machine that has been mass-produced since 2010, since spring. Its world premiere took place in Tokyo in 2009. The company began to accept orders for production from April 1 next year. So, the model is quite interesting, and I would like to tell more about it
All-terrain vehicle "Kharkovchanka": device, specifications, operating features and reviews with photos

All-terrain vehicle "Kharkivchanka": specifications, photos, operating features, pros and cons. Antarctic all-terrain vehicle "Kharkovchanka": device, layout, history of creation, maintenance, reviews. Modifications of the all-terrain vehicle "Kharkovchanka"
Box DSG - reviews. DSG robotic gearbox - device, principle of operation, prices

As you know, there are only a few types of transmissions in the world - mechanical, automatic, tiptronic and CVT. Each of them differs in its design and principle of operation. However, a few years ago, German engineers managed to combine "automatic" with "mechanics". As a result, this invention was called the DSG box. What is this transmission and what features does it have? All this later in our article
How does a car thermostat work? Operating principle

No modern car is complete without a cooling system. It is she who takes on all the heat emanating from the engine during the processing of the combustible mixture
How to use the variator: device, principle of operation, operating tips

There are many types of transmissions in the automotive world. The vast majority are, of course, mechanics and automatic transmission. But in third place was the variator. This box can be found on both European and Japanese cars. Often, the Chinese also put the variator on their SUVs. What is this box? How to use the variator? Consider in our today's article