2026 Author: Erin Ralphs | ralphs@carsalmanac.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 21:14:14
The solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that is controlled by electric current. The latter passes through an electromagnet (a coil wound around the core), as a result of which a magnetic field is formed. By its action, it can open and - vice versa - close the solenoid valve.

In general, this mechanism is used to regulate the flow of liquids and gases. Most often it is used in the agricultural sector (irrigation systems) and for industrial purposes. It is also indispensable in cars.
The design of this mechanism includes the following parts:
- Solenoid coil.
- Pilot hole.
- Solenoid valve poppet.
- Closing spring.
- Valve coil anchor.
- Main flow port.
- Membrane amplifier diaphragm.
- Alignment flow port mechanism.
- Forced valve opening system thatactuated by means of a spring.
Solenoid valve of the 2109th VAZ and its principle of operation
In this mechanism, a certain mechanical force is generated, created by an electromagnetic coil (it converts electricity into magnetic field energy.) As a result, the electromagnetic valve changes its position - it can close and open. At the inlet, this part has an inlet pipe through which gas or liquid passes into the mechanism.
The VAZ solenoid valve includes a rubber (rarely plastic) membrane. It is pressed into the intake pipe and can regulate the flow of incoming fluid. Its front side consists of a sealing ring, which at the right time prevents the flow from entering the mechanism. The membrane is most often mounted on metal springs fixed on the back of the valve.

The position of this mechanism depends on the metal rod, which is placed under the coil. When the latter is excited, the rod moves away under the influence of a magnetic field, and at this time the sealing ring moves away from the membrane. Thus, the flow of gas or liquid passes into the solenoid valve. When the coil is disengaged, the diaphragm is spring-loaded against the inlet sealing surface.
Valve pressure
This part, unlike conventional pumps that perform a similar function, does not have any mechanical devices through which the gas flow passes into the system. That is why it is so importantobserve the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet inlet of the valve. In order for the liquid to pass through the solenoid valve, a higher pressure must be formed in the inlet pipeline than in the outlet.

If this value is the same at both ends of the mechanism, the thread will no longer pass to the working environment. Most modern valves have this principle of operation, except for direct-acting devices (they can transfer gas and liquid regardless of the pressure in the pipelines).
Recommended:
Electro-turbine: characteristics, principle of operation, pros and cons of work, do-it-yourself installation tips and owner reviews
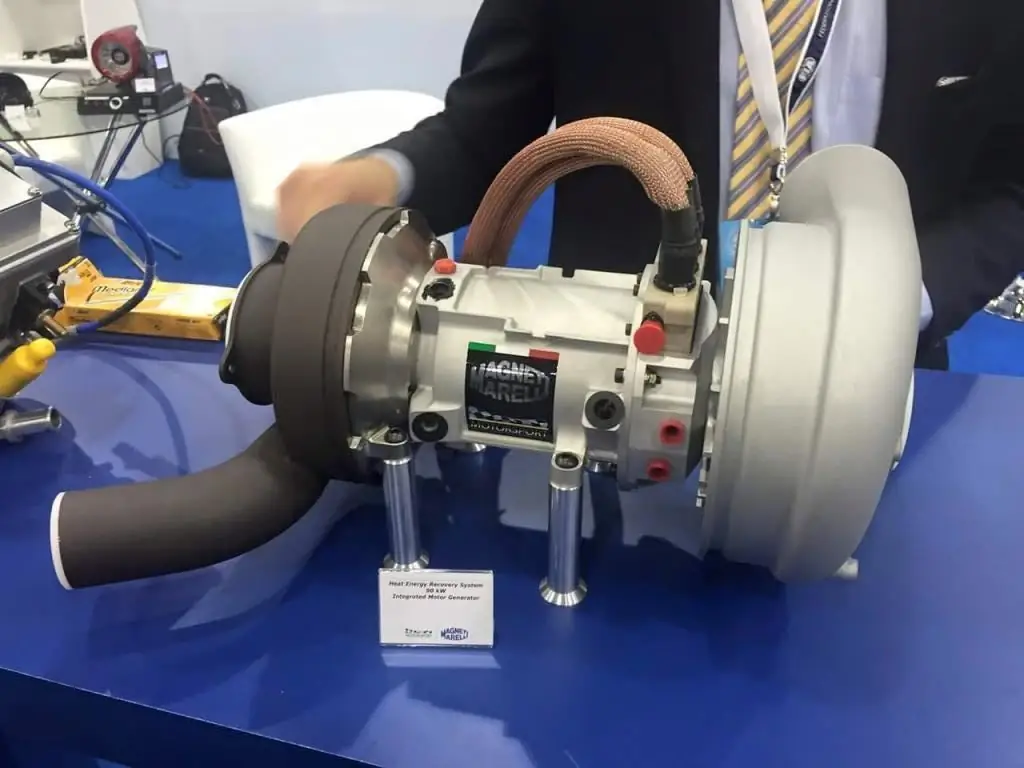

Electric turbines represent the next stage in the development of turbochargers. Despite significant advantages over mechanical options, they are currently not widely used on production cars due to the high cost and complexity of the design
Valve knock: principle of operation, characteristics, causes of knocking, diagnostics and troubleshooting

The gas distribution mechanism is an integral part of any internal combustion engine. The timing system includes several elements, including valves. These parts contribute to the intake of a combustible mixture and the subsequent release of gases from the combustion chamber. On a serviceable motor, the valves should not make any sounds. But what to do if there is a knock of valves? The reasons for this phenomenon and methods for troubleshooting - later in our article
Where is the PCV valve located? Characteristics and principle of operation
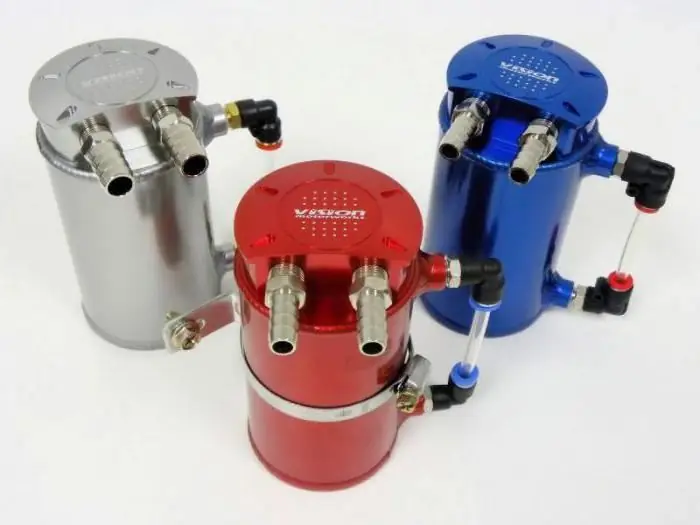

PCV - forced crankcase ventilation system. The functioning of the power unit of the car largely depends on its condition. The main task of this system is the removal of crankcase gases from the engine. They are available in all power units, regardless of their novelty and service life. The only difference between them is the composition and quantity
Carburetor and injector: difference, similarities, advantages and disadvantages of carburetor and injection engines, principle of operation and expert reviews
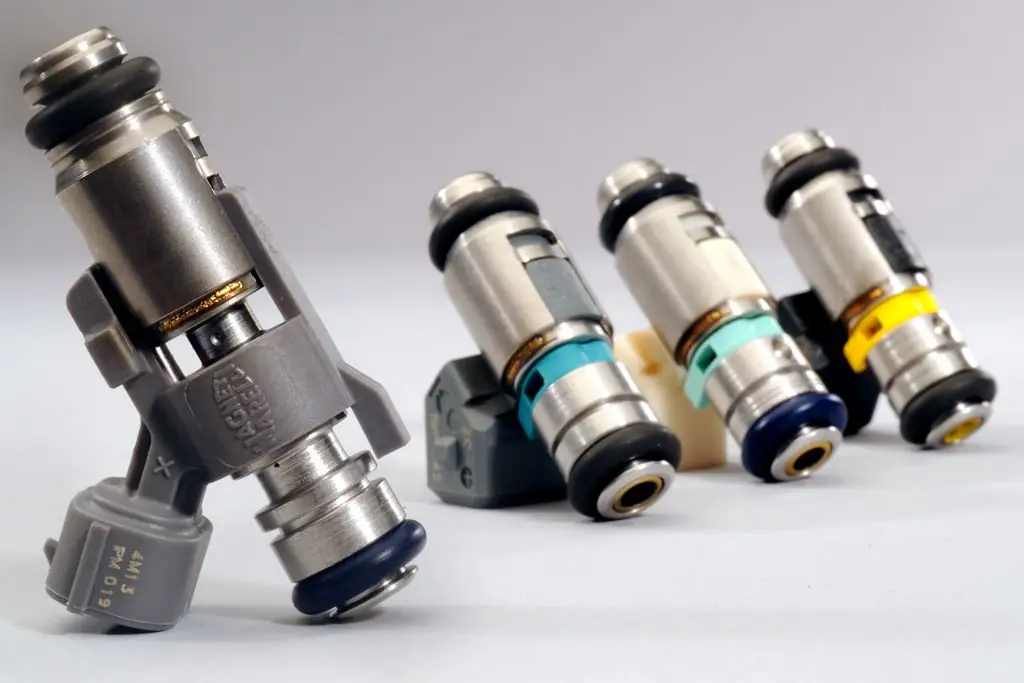

For more than a hundred years, the car has firmly established itself in our lives. During this time, managed to become a familiar, everyday means of transportation. Let's see what the difference is between a carburetor and an injector, what advantages and disadvantages they have
Compression and compression ratio: difference, principle of operation, similarities and differences
Does every vehicle owner clearly understand the difference between compression and compression ratio? Meanwhile, this is by no means the same thing, as some motorists (often beginners) believe, due to little experience. This should be understood at least in order to be able to fix a slight malfunction on your own, without the help of a qualified specialist. In addition, it will be the accumulation of personal experience, which in any case will not hurt

