2026 Author: Erin Ralphs | ralphs@carsalmanac.com. Last modified: 2025-01-22 21:14:11
The history of the navies of the leading powers and significant naval battles since the 19th century is inextricably linked with destroyers. Today, these are no longer those nimble, high-speed ships with a small displacement, a striking example of which is the Zamw alt, a type of US destroyer, which entered sea trials at the very end of 2015.
What are destroyers
A destroyer, or in short, a destroyer, is a class of warships. Multi-purpose high-speed maneuverable ships were originally intended to intercept and destroy enemy ships with artillery fire while guarding a squadron of heavy slow-moving ships. By the beginning of the First World War, the main purpose of destroyers was torpedo attacks on large enemy ships. The war expanded the scope of the destroyers' tasks; they are already serving for anti-submarine and air defense, as well as amphibious landings. Their importance in the fleet began to grow, their displacement and firepower increased significantly.
Today they also serve to fight submarines, ships and aircraft (aircraft, missiles) of the enemy.
Destroyers carrysentinel service, can be used for reconnaissance, provide artillery support during the landing of troops and lay minefields.
At first, a class of light ships appeared, their seaworthiness was low, they could not operate autonomously. Mines were their main weapon. To combat them, so-called fighters appeared in many fleets - small high-speed ships for which torpedoes of the early 20th century did not pose any particular danger. Later, these ships were called the destroyer.
Destroyer - because torpedoes before the revolution were called self-propelled mines in Russia. Squadron - because they guarded squadrons and acted as part of them in the sea and ocean zone.
Prerequisites for creating a class of destroyers
Torpedo weapons in service with the British navy appeared around the last quarter of the 19th century. And the first destroyers were the destroyers Lightning (Great Britain) and Vzryv (Russia) built in 1877. Small, fast and cheap to manufacture, they could sink a large battleship.
Two years later, eleven more powerful destroyers were built for the British fleet, twelve for France, and one each for Austria-Hungary and Denmark.
Successful actions of Russian mine boats during the Russian-Turkish war of 1877-1878. and the development of torpedo weapons led to the creation of the concept of a destroyer fleet, according to which large expensive battleships are not needed for the defense of coastal waters, this task can be solved by many small high-speed destroyer boats with a smalldisplacement. In the eighties of the XIX century, a real "destroyer" boom began. Only the leading maritime powers - Great Britain, Russia and France - had 325 destroyers in their fleets. The fleets of the USA, Austria-Hungary, Germany, Italy and other European countries were replenished with such ships.

The same naval powers at about the same time began to create ships to destroy destroyers and mine boats. These "destroyer fighters" were supposed to be as fast, in addition to torpedoes, have artillery in their armament and have the same power reserve as other large ships of the main fleet.
The displacement of the "fighters" was already significantly greater than that of the destroyers.
The British torpedo ram "Polyphemus" built in 1892, the disadvantage of which was weak artillery armament, the cruisers "Archer" and "Scout", the gunboats of the types "Dryad" ("Halcyon") and "Sharpshooter" are considered to be the prototypes of the destroyers, Jason (Alarm), a large destroyer Swift built in 1894 with interchangeable armament sufficient to destroy enemy destroyers.
The British built for the Japanese an armored destroyer of the first class "Kotaka" of large displacement with a powerful power plant and good weapons, but with unsatisfactory seaworthiness, followed by a ship to combat destroyers "Destructor" commissioned by Spain, where it classified as a torpedo gunboat.
First destroyers
In the eternal confrontation between the British and French navies, the British were the firstbuilt for themselves six ships, which were somewhat different in appearance, but had similar driving characteristics and interchangeable weapons in order to alternately solve the tasks of torpedo bombers or destroyer fighters. Their displacement was about 270 tons, speed - 26 knots. These ships were armed with one 76-mm, three 57-mm guns and three torpedo tubes. Tests have shown that even the simultaneous installation of all weapons does not affect maneuverability and speed. The bow of the vessel was covered with a karalas (“turtle shell”), which protected the conning tower and the main caliber platform installed above it. The breakwaters on the sides of the cabin protected the rest of the guns.
The first French destroyer was built in the last year of the 19th century, and the American one at the very beginning of the next century. In the United States, 16 destroyers were built in four years.
In Russia at the turn of the century, unnamed, so-called numbered destroyers were built. With a displacement of 90-150 tons, they developed a speed of up to 25 knots, were armed with one fixed, two mobile torpedo tubes and a light cannon.
Destroyers became an independent class after the war of 1904-1905. with Japan.
Destroyers of the early 20th century
At the turn of the century, steam turbines came into the design of the power plant of destroyers. This change allows you to dramatically increase the speed of ships. The first destroyer with a new power plant was able to reach a speed of 36 knots during trials.
Then England began to build destroyers that run on oil, not coal. Follow her to liquidfuel began to cross the fleets of other countries. In Russia, it was the Novik project, built in 1910.
The Russo-Japanese war with the defense of Port Arthur and the Battle of Tsushima, in which nine Russian and twenty-one Japanese destroyers clashed, showed the shortcomings of this type of ships and the weakness of their weapons.
By 1914, the displacement of destroyers had grown to 1000 tons. Their hulls were made of thin steel, fixed and single-tube mobile torpedo tubes were replaced by multi-tube ones on a rotating platform, with optical sights fixed on it. Torpedoes have become larger, their speed and range have increased significantly.
The conditions for the rest of sailors and officers of the destroyers' crew have changed. Officers received separate cabins for the first time on the British destroyer River in 1902.
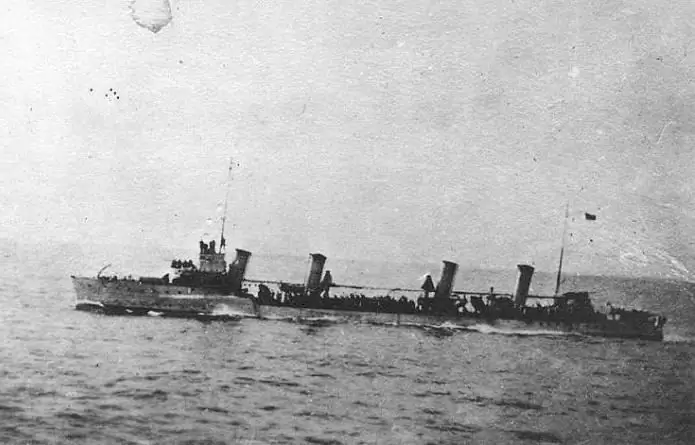
During the war, destroyers with a displacement of up to one and a half thousand tons, a speed of 37 knots, steam boilers with oil nozzles, four triple-tube torpedo tubes and five guns of 88 or 102 mm caliber actively participated in patrolling, raiding operations, setting minefields transported troops. More than 80 British and 60 German destroyers took part in the biggest naval battle of this war - the battle of Jutland.
In this war, destroyers began to perform another task - to protect the fleet from submarine attacks, attacking them with artillery fire or ramming. This led to the strengthening of destroyer hulls, equipping them with hydrophones for detecting submarines and depth charges. First timethe submarine was sunk by a depth charge by the destroyer Llewellyn in December 1916.
Great Britain created a new subclass during the war years - the "destroyer leader", with greater characteristics and weapons than a conventional destroyer. It was intended to launch its own destroyers into the attack, fight against the enemy, control groups of destroyers and reconnaissance at the squadron.
Destroyers between the wars
The experience of the First World War showed that the torpedo armament of destroyers is insufficient for combat operations. To increase the number of volleys in built-in vehicles, six pipes were installed.
Japanese Fubuki-class destroyers can be considered a new stage in the construction of this type of ships. They were armed with six powerful high-elevation five-inch guns that could be used as anti-aircraft guns, and three triple-tube torpedo tubes with Type 93 Long Lance oxygen torpedoes. In the following Japanese destroyers, spare torpedoes began to be placed in the deck superstructure to speed up the reloading of vehicles.
US destroyers of the Porter, Machen and Gridley projects were equipped with twin five-inch guns, and then increased the number of torpedo tubes to 12 and 16, respectively.
French Jaguar-class destroyers already had a displacement of 2,000 tons and 130mm guns.
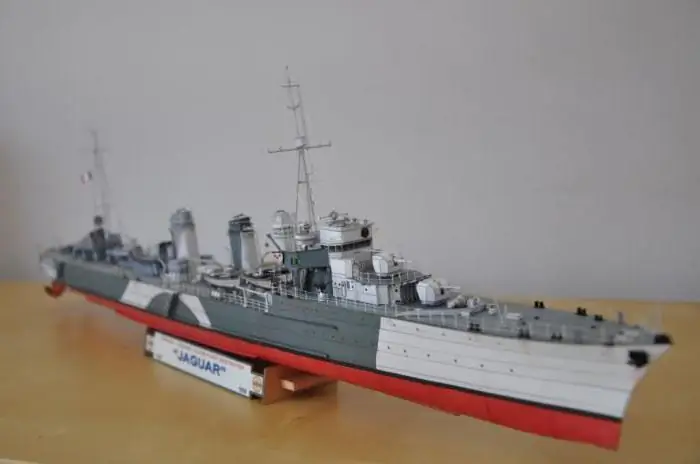

The destroyer leader Le Fantask, built in 1935, had a record speed of 45 knots for that time and was armed with five 138-mm guns and nine torpedo tubes. almost like thatItalian destroyers were just as fast.
In accordance with the Hitler's rearmament program, Germany also built large destroyers, ships of the 1934 type had a displacement of 3 thousand tons, but weak armament. Type 1936 destroyers were already armed with heavy 150mm guns.
The Germans in the destroyers used a steam turbine plant with high pressure steam. The solution is innovative, but it led to serious problems in the mechanics.
In contrast to the Japanese and German programs for the construction of large destroyers, the British and Americans began to create lighter, but more numerous ships. British destroyers of types A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H with a displacement of 1.4 thousand tons had eight torpedo tubes and four 120 mm guns. True, destroyers of the Tribal type with a displacement of more than 1.8 thousand tons were built at the same time with four gun turrets, in which eight twin 4.7-inch guns were installed.
Then the J-type destroyers with ten torpedo tubes and three turrets with six twin guns were launched, and the L-type destroyers, which were equipped with six twin new universal guns and eight torpedo tubes.
The US Benson-class destroyers, displacing 1,600 tons, were armed with ten torpedo tubes and five 127 mm (5-inch) guns.
The Soviet Union before the Great Patriotic War built destroyers according to project 7 and modified 7u, in which the echeloned arrangement of the power plant made it possible to improve the survivability of ships. They developed a speed of 38 knots with a displacement of about 1.9 thousand tons.
Poproject 1/38, six destroyer leaders were built (the lead one was Leningrad) with a displacement of almost 3 thousand tons, with a speed of 43 knots and a cruising range of 2, 1 thousand miles.
In Italy, the leader of the destroyers "Tashkent" with a displacement of 4.2 thousand tons, with a maximum speed of 44 knots and a cruising range of more than 5 thousand miles at 25 knots of speed was built for the Black Sea Fleet.
World War II experience
In the Second World War, aviation took an active part, including in combat operations at sea. Anti-aircraft guns and radars began to be rapidly installed on destroyers. In the fight against already more advanced submarines, bombers began to be used.
Destroyers were "consumables" of the fleets of all warring countries. They were the most massive ships, participated in all battles in all theaters of military operations at sea. German destroyers of that period had only tail numbers.
By the middle of the 20th century, some destroyers of the war era, in order not to build expensive new ships, were modernized specifically to fight submarines.
Also, a number of large ones were built, armed with automatic guns of the main caliber, bombers, radar, ship sonar: Soviet destroyers of project 30 bis and 56, English - "Daring" and American "Forrest Sherman".
Missile era destroyers
Since the sixties of the last century, with the advent of surface-to-surface and surface-to-air missiles, major maritime powers began to build destroyers with guided missile weapons (the Russian abbreviation is URO,English - DDG). These were Soviet Project 61 ships, English ones of the County type, American ships of the Charles F. Adams type.
By the end of the 20th century, the boundaries between destroyers proper, heavily armed frigates and cruisers are blurring.
In the Soviet Union, since 1981, they began to build project 956 destroyers (Sarych or Sovremenny type). These are the only Soviet ships that were originally classified as destroyers. They were intended to combat surface forces and support the landing, and then for anti-submarine and air defense.
The destroyer Persistent, the current flagship of the B altic Fleet, was also built according to project 956. It was launched in January 1991.
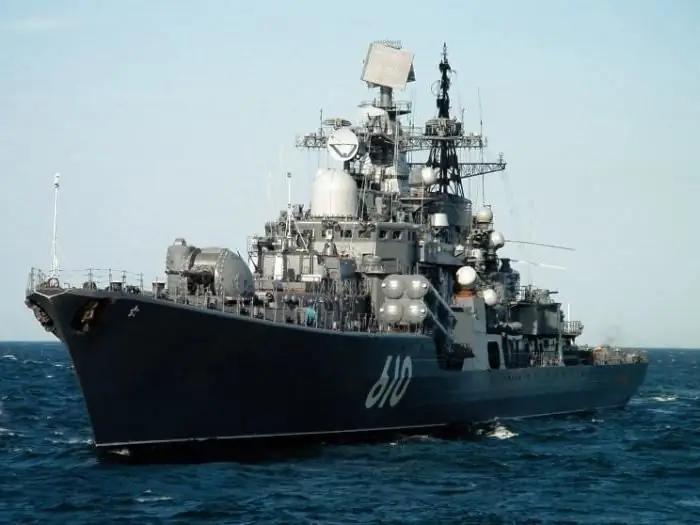

Its total displacement is 8 thousand tons, length - 156.5 m, maximum speed - 33.4 knots, cruising range - 1.35 thousand miles at a speed of 33 knots and 3.9 thousand miles at 19 knots. Two boiler-turbine units give a capacity of 100 thousand liters. s.
The destroyer is armed with Moskit anti-ship cruise missile launchers (two quad), Shtil anti-aircraft missile system (2 mounts), RBU-1000 six-barrel bombers (2 mounts), two twin 130 mm gun mounts, six-barrel AK-630 (4 installations), two twin 533 mm torpedo tubes. On board the ship is a Ka-27 helicopter.
Of the newest ones already built, until recently, the destroyers of the Indian fleet were. Delhi-class ships are armed with anti-ship missiles withrange of 130 km, Shtil (Russia) and Barak (Israel) air defense systems for air defense, Russian RBU-6000 anti-submarine rocket launchers for anti-submarine defense and five torpedo guides for torpedoes with a caliber of 533 mm. The helipad is designed for two Sea King helicopters. It is planned to soon replace these ships with destroyers of the Kolkata project.
Today, the destroyer DDG-1000 Zumw alt of the US Navy took over the palm.
Destroyers in the 21st century
In all major fleets, there have been general trends in the construction of new destroyers. The main one is the use of combat control systems similar to the American Aegis (AEGIS), which is designed to destroy not only aircraft, but also ship-to-ship and air-to-ship missiles.
When creating new ships, Ste alth technology should be used: radar-absorbing materials and coatings should be used, special geometric shapes should be developed, such as, for example, the USS Zumw alt-class destroyer.
In the new destroyers, the speed should also increase, due to which habitability and seaworthiness will increase.
Modern ships have a high level of automation, but it should also increase, which means that the proportion of auxiliary power plants should increase.
It is clear that all these processes lead to an increase in the cost of building ships, so a qualitative increase in their capabilities should occur at the expense of a reduction in numbers.
Destroyers of the new century shouldsurpass in size and displacement all the ships of this type that have been available to date. The new destroyer DDG-1000 Zumw alt is considered the record holder in terms of displacement, it is 14 thousand tons. Ships of this type were planned to enter the US Navy in 2016, the first of them has already entered sea trials.
By the way, domestic destroyers of project 23560, which, as promised, will begin to build by 2020, will already have a displacement of 18 thousand tons.
Russian project of a new destroyer
According to project 23560, which, according to media reports, is in the preliminary design stage, it is planned to build 12 ships. The destroyer "Leader", 200 meters long and 23 meters wide, should have an unlimited cruising range, be in autonomous navigation for 90 days, and reach a maximum speed of 32 knots. The ship is supposed to have a classic layout using Ste alth technologies.

The promising destroyer of the Leader project (surface ship of the ocean zone) will most likely be built with a nuclear power plant and should carry 60 or 70 ste alth-based cruise missiles. It is supposed to hide in the mines and anti-aircraft guided missiles, of which there should be only 128, including the Polyment-redoubt air defense system. Anti-submarine weapons should consist of 16-24 guided missiles (PLUR). The destroyers will receive a 130 mm A-192 Armat universal gun mount and a landing pad for twomultipurpose helicopters.
All data is still tentative and may be further refined.
Navy representatives believe that Leader-class destroyers will be universal ships, performing the functions of destroyers themselves, anti-submarine ships and, perhaps, Orlan-class missile cruisers.
Destroyer "Zamvolt"
Zumw alt-class destroyers are a key element of the US Navy's 21st Century Surface Combatant (SC-21) Surface Combatant program.
The Russian destroyer of the "Leader" type is a question, perhaps not far away, but of the future.
But the first destroyer of the new type DDG-1000 Zumw alt has already been launched, and in early December 2015, its factory tests began. The destroyer's distinctive appearance has been described as futuristic, with its hull and superstructure covered in radar-absorbing materials nearly three centimeters (1 inch) thick, and the number of protruding antennas reduced to a minimum.
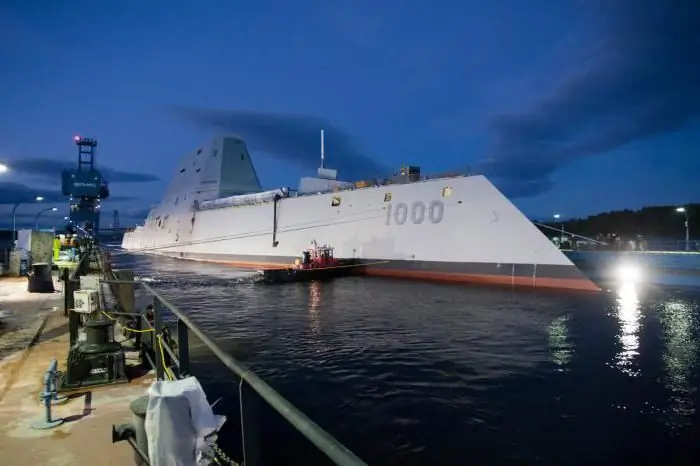

The Zumw alt-class destroyer series is limited to just 3 ships, two of which are still in various stages of construction.
Destroyers of the Zamvolt type, 183 m long, with a displacement of up to 15 thousand tons and a combined power of the main power plant of 106 thousand liters. With. will be able to reach speeds up to 30 knots. They have a powerful radar potential and are able to detect not only low-flying missiles, but also terrorist boats at long distances.
Destroyers are armed with 20 MK vertical launchers57 VLS, capable of carrying 80 Tomahawk, ASROC or ESSM missiles, two Mk 110 57mm fast-firing anti-aircraft guns, two 155mm AGS cannons with a range of 370 km, two tubular 324mm torpedo tubes.
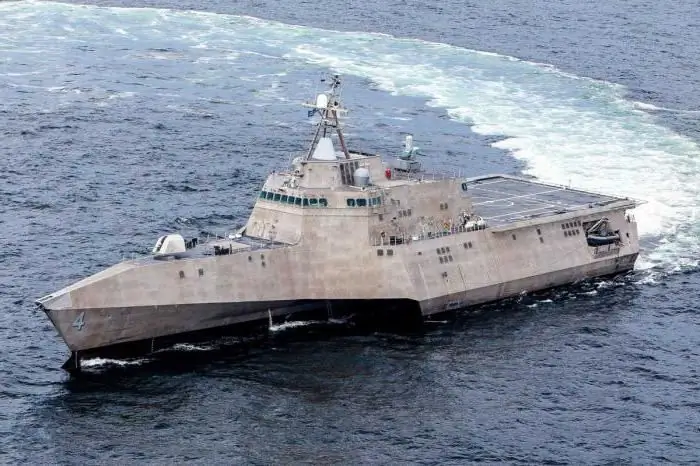

Ships can carry 2 SH-60 Sea Hawk helicopters or 3 MQ-8 Fire Scout unmanned aerial vehicles.
"Zamvolt" - a type of destroyers, the main task of which is to destroy enemy coastal targets. Also, ships of this type can effectively fight enemy surface, underwater and air targets and support their own forces with artillery fire.
"Zamvolt" is the embodiment of the latest technology, it is the latest destroyer launched to date. The projects of India and Russia have not yet been implemented, and this type of ship, it seems, has not yet become obsolete.
Recommended:
What kind of oil to fill in the Niva-Chevrolet: types, characteristics, composition of oils and their effect on the operation of a car

The article provides detailed information about the oil that is best filled in the Chevrolet Niva. These are popular manufacturers, varieties and features of oils, as well as detailed instructions for replacing old oil with a new one
Types of spark plugs, their characteristics, differences and tips for choosing

What types of spark plugs can the modern automotive market offer motorists? Unfortunately, few people understand the importance of such irreplaceable parts among vehicle owners. Meanwhile, they have a set of important characteristics that everyone needs to know about
Starting engine: concept, types, technical characteristics, starting rules and operating features

The starter motor, or "starter", is a 10 horsepower carbureted internal combustion engine that is used to help start diesel tractors and machinery. Similar devices were previously installed on all tractors, but today a starter has come to replace them
Car operation is Types, characteristics, categories, depreciation and fuel consumption calculations, features of work and technical use

Logistics of road transport is an important factor in technical operation systems and is a process of supplying automobile enterprises with rolling stock, units, spare parts, tires, batteries and materials necessary for their normal operation. Proper organization of logistics plays a crucial role in improving the use of vehicles by keeping them in good condition
Badges of car brands and names. German, American and Chinese car brands and their badges

Badges of brands of cars - how diverse they are! With and without a name, intricate and simple, multi-color and plain … And all are very original and interesting. So, since German, American and Asian cars are the most common and in demand, then using the example of their best cars, the topic of the origin of emblems and names will be revealed

